
Abecedarium
A text, usually in the form of verse, in which every line or every alternate line starts with a consecutive letter of the alphabet. Used as a tool for teaching young children how to read.
Read more



Battledore

Book of secrets
Books of secrets or recipe books are ‘treatises that professed to reveal the “secrets of nature” to anyone who could read’ (Eamon 1994, 3).
Read more
Broadsheet (broadside)
Broadsheets (or broadsides) is a portmanteau term referring to a form of prints consisting of only a single sheet, printed on one side only in the case of broadsides.
Read more


Catechism
The catechism is an exposition of Christian doctrine, or oftentimes rather an ideal of what the true doctrine should be. Such texts quickly became participants in the fierce political and religious struggles between Catholics and Protestants over the correct interpretation of the faith.
Read more
Catechism primer
The label catechism primer is used to define a wide range of materials aimed at teaching to read and contextually providing religious education.
Read more

Children’s book and schoolbook
Apart from schoolbooks, in most Northern European countries a distinct market for children’s literature meant for entertainment did not establish until the late 17th or 18th century, and in Southern Europe by the 19th century.
Read more
Chronicle/Chronology
Overview of events described in chronological order, often starting from Creation until the most recent times. Part of these events were biblical or classical, others were related to more recent European or national (sometimes even regional) history.
Read more


Criminal narrative
Criminal narratives are stories about criminals, be it fictional or non-fictional. This genre comprises many forms such as criminal biographies, dying speeches, murder and execution ballads, and penny prints.
Read more
Devotional literature
Devotional literature accounted for a major stream of steady sellers across Europe from the early days of print onwards.
Read more

Game (printed on paper)
Printed materials designed for play, usually according to prescribed rules.
Read more



History print


Household manual
Didactic texts that advised on practical how-to knowledge (e.g. recipes, husbandry, domestic labour), on devotional practices within the home, and/or on the appropriate conduct for husbands, wives, and other household members.
Read more
How-to book
Early modern how-to books are a category for which no unified terminology is in use. They provided practical instruction, often combined with some more theoretical or general background knowledge, in fields as varied as medicine, carpentry, horticulture, navigation, mining, cooking, calligraphy, embroidery.
Read more
Indulgence



Libel/pasquil
Libels and pasquils were types of pamphlets, (often short) polemical writings with a satirical or outright biting tone.
Read more
Lives of saints

Lottery ticket
Lottery was a game of chance in the early modern period. A lottery ticket was bought in order to participate in a lottery. In these days two forms of lotteries were current in Europe: the lotto and the class lottery.
Read more
Martyr story
Amidst the religious controversies of the 16th and 17th centuries, especially in Germany, the Low Countries, England, and France, the lives and especially the deaths of contemporary martyrs were the subject of different kinds of publications.
Read more
Medical literature
Medical text types overlapped and merged in many ways (e.g. theoretical explanations and practical remedies, preventive and curative medicine), and many kinds of compilations of medical knowledge appeared.
Read more


New Year prints
Various types of print related to Christmas and the new year circulated in the early modern period.
Read more
News pamphlet
News pamphlets are small printed items containing just a single news fact or event. Across Europe, they were an important means of distributing printed news in the era before periodicals
Read more



Nouvelle
Term used in French, English, Dutch (nouvelle) and Italian (nuova) to denote a single piece of news, similar in use to tiding and report. Predating, and subsequently running parallel with, the early modern use of nouvelle in a news context, the term was used to indicate a literary genre of short narrative prose.
Read more
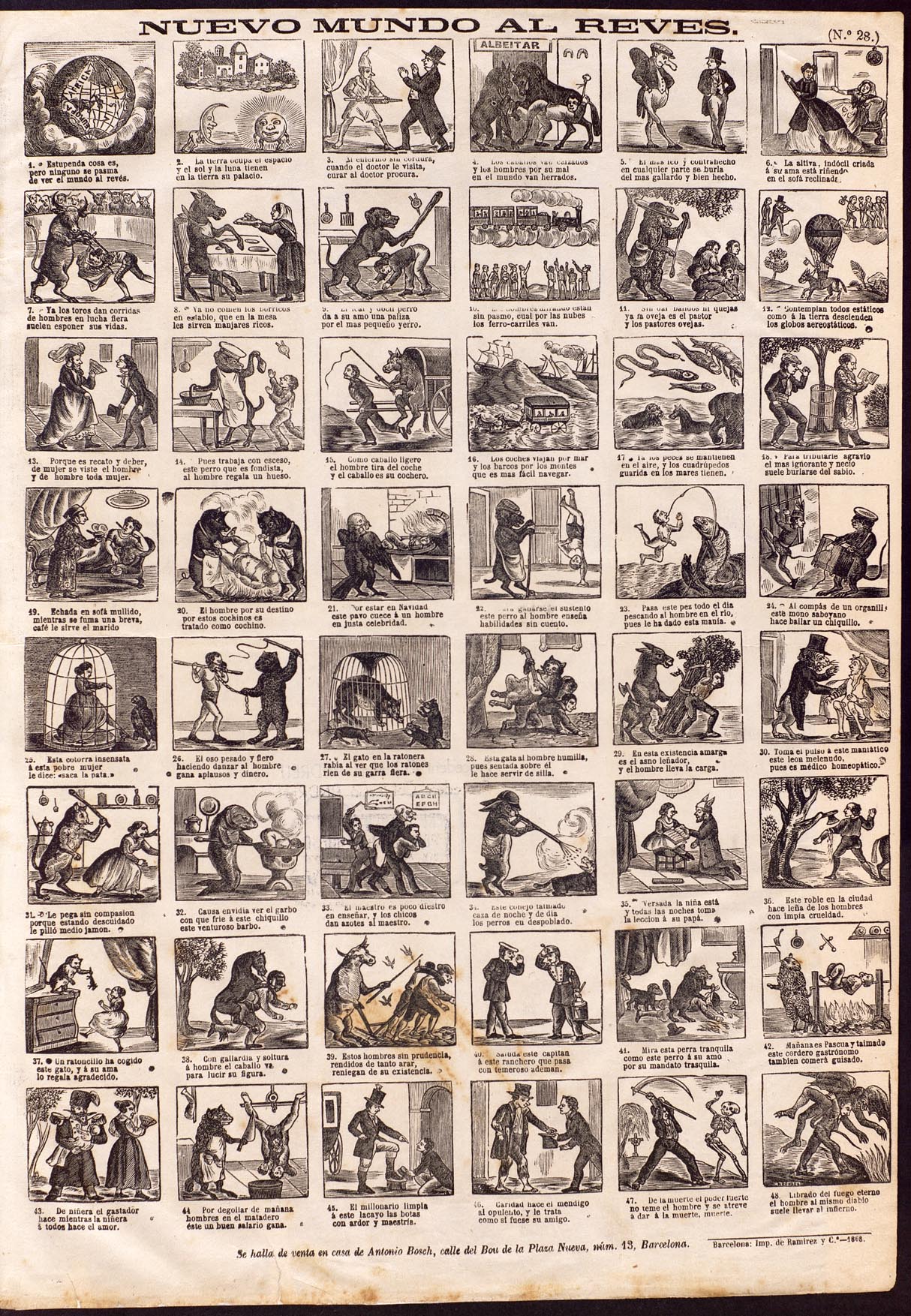




Penny print
Penny prints are cheap broadsides, printed on one side and illustrated with 8 to 48 woodcuts. Rhyming captions below the images either narrated the story or explained the (non-fictional) pictures.
Read more
Plague sheet/book
The plague, probably the most-feared disease in early modern Europe, generated an ongoing stream of printed materials, booklets as well as printed images, especially at times of outbreaks.
Read more
Playbill/Playbook
The term playbill is used for a bill, placard or poster that advertised plays and was intended for public display. They usually also gave the names of the actors. Playbooks contained the theatre texts themselves.
Read more
Prayer book
Prayer books were commonly considered aids for the conduct of church service or for personal prayer. As such they were not wholly unambiguously popular print.
Read more
Proclamation
Proclamations or ordinances, usually from the state government, notified the population of official decrees and laws.
Read more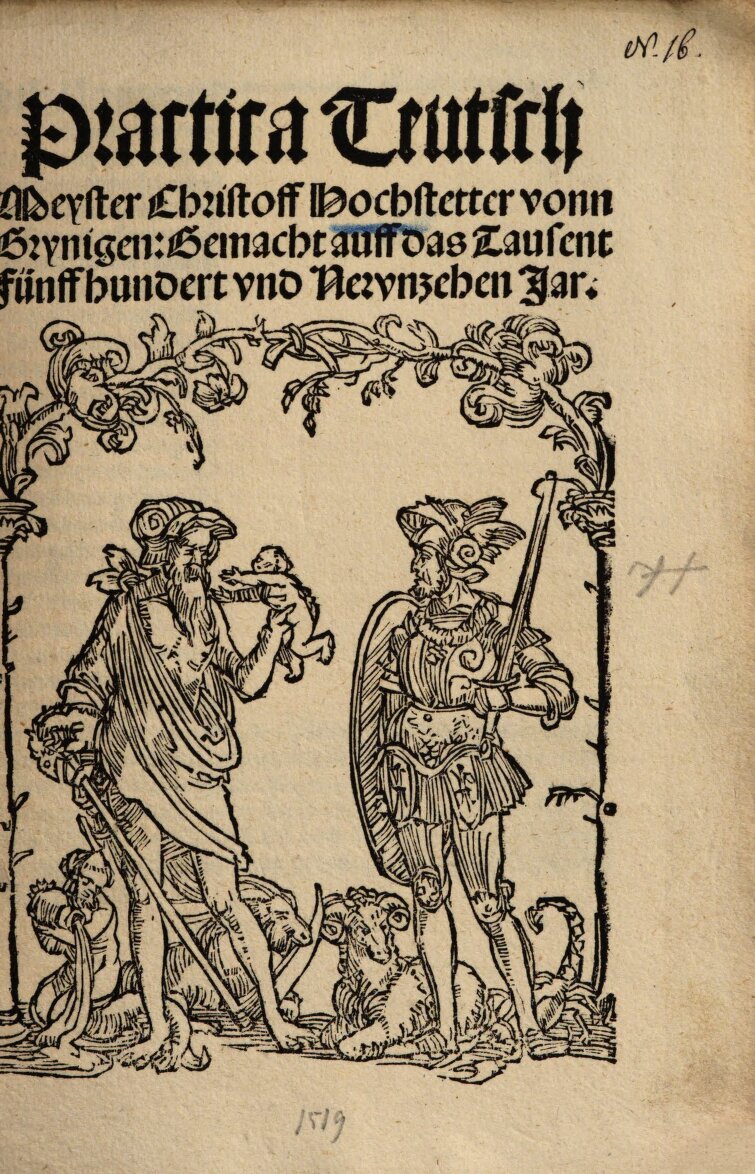
Prognostication
Booklet in almanac form or part of an almanac containing (almost) exclusively predictions for the coming year, describing seasons, months, expected harvests, foreseeable diseases, wars, etc.
Read more
Prose romance

Recipe book

Regimen book
Regimens instructed people in the management of the six non-natural things from which health depends. These are: food and drink, sleep, exercise, the air one breathes, emotions (or ‘passions’) and evacuations (including hygiene).
Read more



Rooster primer
The label “rooster primer” is used to refer to a reading primer with the image of the rooster on a prominent place of the booklet. Printed since the 1570s in Central Europe and soon after in Northern Europe, in some countries the history of this kind of primers extends into the present. Whereas the position…
Read more
Saint’s life
Saints’ lives were the subject of many kinds of popular publications, ranging from ballads and single-sheet images (e.g. devotional images, penny prints) to longer stories (e.g. in chapbooks), sermons, prayers, and collections of hagiographies.
Read more
Schoolbook


Song/Song book


Topical poetry
Topical or occasional poetry was written in response to an event in the family (birth, marriage, death) or public sphere (battle, commemoration), or on the occasion of a poetry contest (e.g. of rhetoricians, or the Spanish justas poéticas).
Read more
Travel accounts and guides
Descriptive accounts or literary writings by travellers.
Read more
